Salivary glands play a vital role in maintaining oral health and overall well-being by producing and secreting saliva. However, these glands can sometimes be afflicted by various disorders that impact their functionality and lead to discomfort and health issues. Sialendoscopy, a minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure, has emerged as a valuable tool in the management of salivary gland disorders. This comprehensive overview delves into the world of sialendoscopy and its applications in the context of salivary gland disorders.
Salivary Gland Disorders: Salivary gland disorders encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the normal functioning of the salivary glands. These disorders can be broadly categorized into inflammatory, obstructive, and neoplastic conditions. Inflammatory disorders, such as sialadenitis and autoimmune diseases, lead to glandular inflammation and subsequent reduction in saliva production. Obstructive disorders, such as salivary stones (sialolithiasis), result from the formation of calcified deposits within the ducts, hindering the flow of saliva. Neoplastic conditions involve the development of tumors within the salivary glands, which can be either benign or malignant.
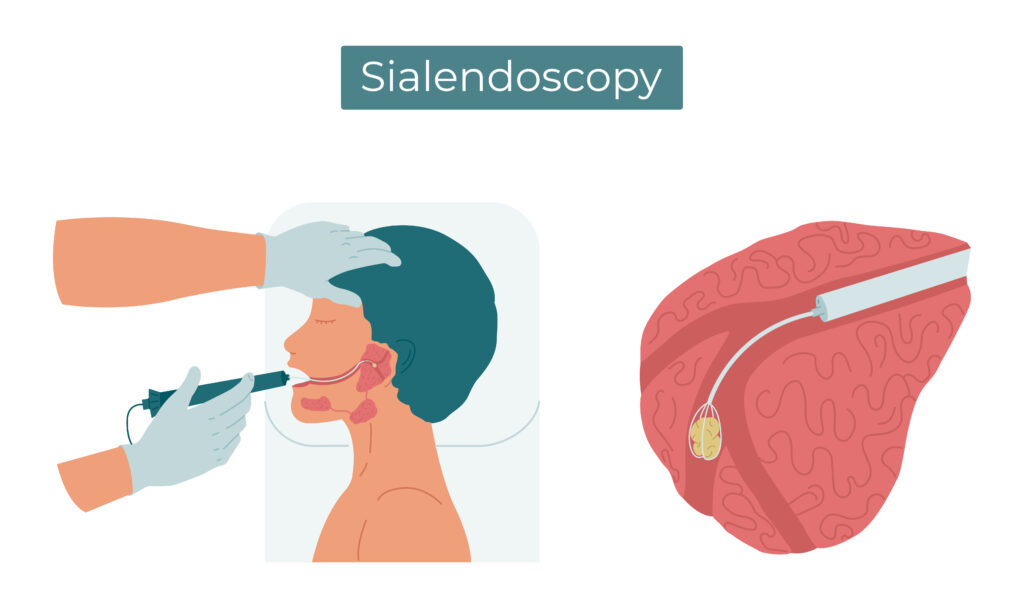
Sialendoscopy: Sialendoscopy is a relatively recent advancement in the field of otolaryngology (ear, nose, and throat) that offers a minimally invasive approach for the diagnosis and treatment of salivary gland disorders. It involves the use of a thin, flexible endoscope, equipped with a camera and light source, to visualize the interior of the salivary gland ducts and the glandular tissue. This procedure can be performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and the complexity of the case.
Procedure: The sialendoscopy procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia: The patient is administered local or general anesthesia to ensure comfort and minimize discomfort during the procedure.
- Cannulation: A small incision is made near the affected salivary gland, and a micro-endoscope is inserted into the salivary duct system.
- Visualization: The endoscope provides real-time visualization of the interior of the ducts and glandular tissue, allowing the surgeon to identify any abnormalities or obstructions.
- Treatment: Depending on the specific disorder, various interventions can be performed using specialized instruments inserted through the endoscope. These interventions include removing salivary stones, dilating strictures, and even performing biopsies for neoplastic lesions.
- Recovery: Sialendoscopy is minimally invasive, resulting in reduced postoperative pain and quicker recovery times compared to traditional surgical approaches.
Applications: Sialendoscopy has revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment of salivary gland disorders:
- Salivary Stone Removal: Sialolithiasis, or salivary stones, can cause excruciating pain and obstructed saliva flow. Sialendoscopy enables the direct visualization and removal of these stones, relieving symptoms and restoring normal glandular function.
- Dilation of Strictures: In cases of strictures (narrowing) within the salivary ducts, sialendoscopy allows for the gentle dilation of these areas, facilitating improved saliva flow.
- Tumor Biopsy and Assessment: Sialendoscopy aids in the evaluation of suspicious lesions within the salivary glands. Biopsies can be performed under direct visualization, helping to determine whether a tumor is benign or malignant.
- Treatment of Inflammatory Conditions: Inflammatory disorders, such as chronic sialadenitis, can be managed through sialendoscopy-guided procedures, which can help alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrent inflammation.
Advantages: Sialendoscopy offers several advantages over traditional surgical approaches:
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure is minimally invasive, resulting in smaller incisions, reduced pain, and faster recovery times.
- Preservation of Gland Function: Sialendoscopy procedures aim to preserve the function of salivary glands by addressing disorders without the need for gland removal.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Direct visualization of the glandular tissue allows for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
- Outpatient Procedure: In many cases, sialendoscopy can be performed on an outpatient basis, minimizing hospital stays.
Sialendoscopy has revolutionized the management of salivary gland disorders by providing a minimally invasive approach to diagnosis and treatment. This innovative technique has improved patient outcomes, reduced pain and recovery times, and allowed for the preservation of salivary gland function. As technology and techniques continue to advance, sialendoscopy is poised to play an increasingly pivotal role in the field of otolaryngology and the treatment of salivary gland disorders.

